GraphQL
The GraphQL type system describes the capabilities of a GraphQL server and is used to determine if a query is valid. This schema is defined with the GraphQL Schema Definition Language (SDL) and is much easier to read and write than a JSON schema.
The graphql input provider translates a GraphQL schema to a JSON schema. This way you can define
the shape of your configuration in a GraphQL schema.
Configuration
{
"component": {
"inputs": [
{
"type": "graphql"
}
]
}
}Example
Create a schema.graphql file in your components folder.
type Configuration {
requiredField: String!
optionalField: String
nestedType: NestedType!
enumSupport: Kind!
interfaceSupport: ExampleInterface!
unionSupport: ExampleUnion!
date: Date
uuid: UUID
regex: Regex
withDefault: String @defaultValue(value: "default value")
withVariableDefault: String @defaultValue(value: "$shared:common.authority")
}
type NestedType {
nestedValue: String!
}
enum Kind {
KindA
KindB
}
interface ExampleInterface {
interfaceField: String!
}
type ExampleA implements ExampleInterface {
interfaceField: String!
typeAField: String!
}
type ExampleB implements ExampleInterface {
interfaceField: String!
typeBField: String!
}
union ExampleUnion = ExampleA | ExampleBWhen we now run a confix build in the Website folder, the GraphQL schema is translated to a
schema.json file.
The appsettings.json file is also initialized and looks like this:
{
"Website": {
"requiredField": null,
"nestedType": {
"nestedValue": null
},
"enumSupport": null,
"interfaceSupport": null,
"unionSupport": null,
"withDefault": "default value",
"withVariableDefault": "$shared:common.authority"
}
}GraphQL Type System Support
The GraphQL type system is very powerful and supports Object, Interface, Union, Enum,
Input Object and Scalar types. The graphql input provider supports all of
these types except InputObject.
The Query type of the GraphQL schema is the entry point for the configuration. If you do not have
a Query type, the first object type is used as the entry point.
Nullability
In GraphQL all fields are nullable by default. If you want to make a field required, you have to
append an exclamation mark to the type. The graphql provider leverages this and makes all fields
that are not nullable in the GraphQL schema required in the JSON schema.
Default Values
In common components you may also want to define default values for fields. You for example define a shared variable as the default value and all projects that reference the component will also use this value as soon as they are initialized
type Configuration {
authority: String! @defaultValue(value: "$shared:common.authority")
}Object Types
type Example {
stringField: String!
intField: Int!
}These are translated to JSON objects. The fields of the object type are translated to the properties.
Learn more about Object Types (opens in a new tab).
Enum Types
enum Example {
KindA
KindB
}A enum type in GraphQL is a special kind of scalar that is restricted to a particular set of allowed values Enum types are translated to JSON strings. The enum values are used as the allowed values.
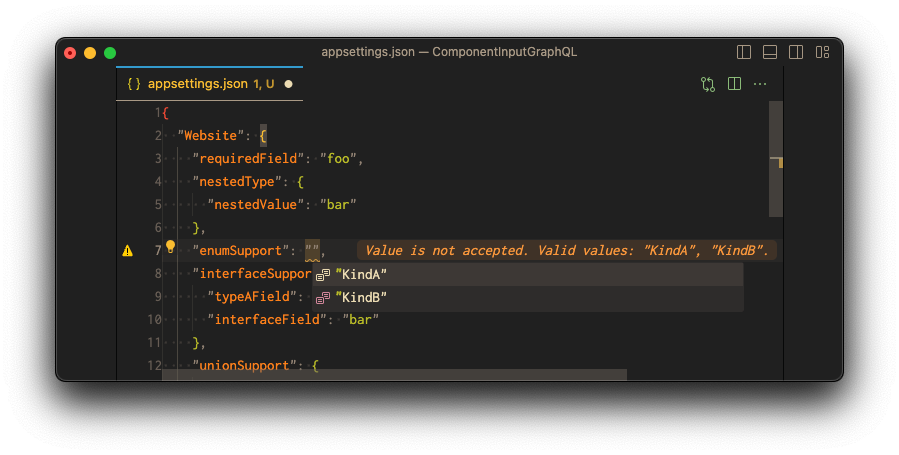
Learn more about Enum Types (opens in a new tab).
Union Types
type ExampleA {
stringField: String!
}
type ExampleB {
intField: Int!
}
union Example = ExampleA | ExampleBUnion types are very similar to interfaces, but they don't get to specify any common fields between the types.
Union types are translated to JSON objects. The union types are translated to a oneOf schema.
This means all properties of the union types are allowed in the JSON schema if type type is not clear:
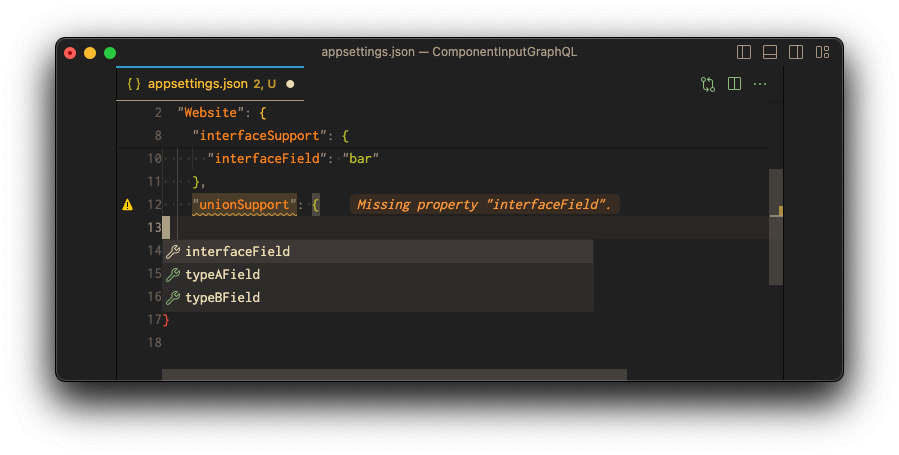 But as soon as the type is clear, only the properties of the specific type are allowed:
But as soon as the type is clear, only the properties of the specific type are allowed:
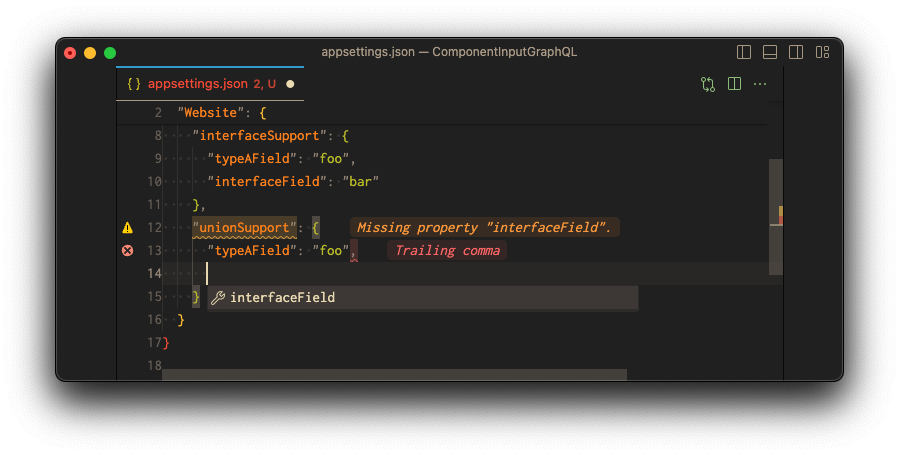
Learn more about Union Types (opens in a new tab).
Interface Types
interface Example {
stringField: String!
}
type ExampleA implements Example {
stringField: String!
}
type ExampleB implements Example {
stringField: String!
intField: Int!
}Interfaces are useful for defining fields that you want to include in multiple types. Interfaces are
translated to JSON objects. The interface types are translated to a oneOf schema.
This means all properties of the interface types are allowed in the JSON schema if type type is not
clear:
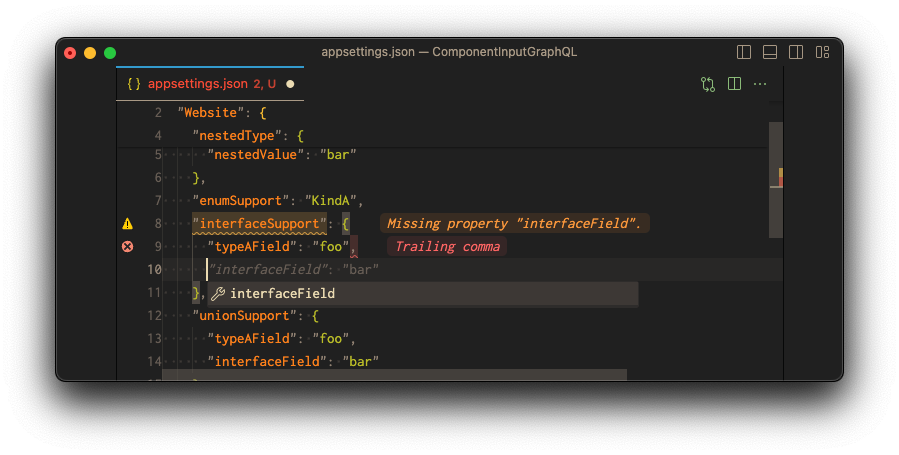 But as soon as the type is clear, only the properties of the specific type are allowed:
But as soon as the type is clear, only the properties of the specific type are allowed:
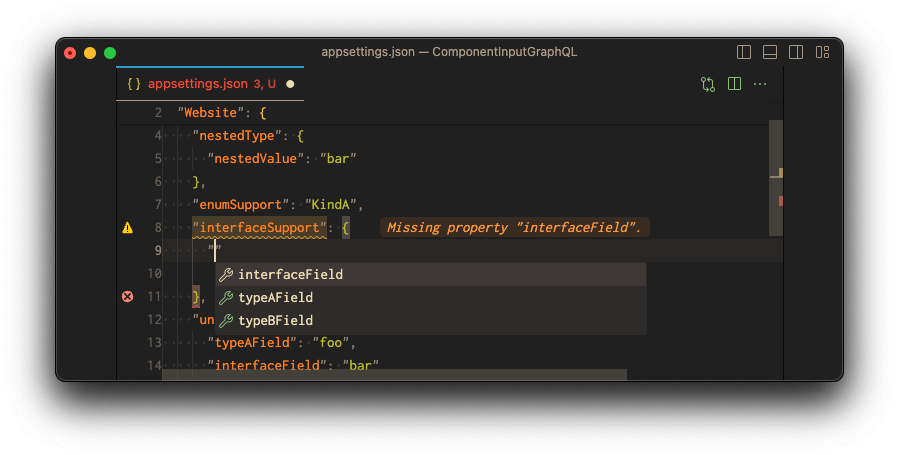
Scalars
scalar RegexGraphQL Scalars represent primitive leaf values like String or Int. The graphql provider
translates these scalars to JSON primitives as per the Json Schema standards, with some scalars
having an additional format specification for validation purposes.
Here's the mapping from GraphQL scalars to JSON primitives and their respective formats:
| GraphQL Scalar | JSON Primitive | Format |
|---|---|---|
Int | integer | |
Long | integer | |
Float | number | |
Double | number | |
Boolean | boolean | |
String | string | |
Uuid | string | uuid |
UUID | string | uuid |
Guid | string | uuid |
GUID | string | uuid |
Date | string | date |
DateTime | string | date-time |
TimeSpan | string | time-span |
Duration | string | duration |
EmailAddress | string | email |
IdnEmailAddress | string | idn-email |
HostName | string | hostname |
IdnHostName | string | idn-hostname |
IpAddress | string | ipv4 |
Ip | string | ipv4 |
Ipv4 | string | ipv4 |
Ipv6 | string | ipv6 |
Uri | string | uri |
Url | string | uri |
JsonPointer | string | json-pointer |
RegEx | string | regex |
Regex | string | regex |
Json | object | json |
Any | object | json |
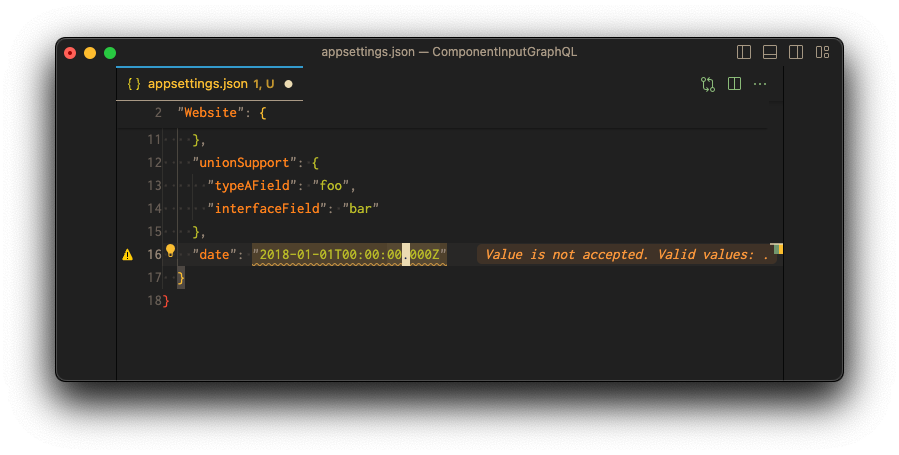
Here is an example of the Date scalar. The format property is set to date so it rejects a date
time value.